CSE559A Lecture 6
Continue on Light, eye/camera, and color
BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function)
Diffuse Reflection
-
Dull, matte surface like chalk or latex paint
-
Most often used in computer vision
-
Brightness does depend on direction of illumination
Diffuse reflection governed by Lambert’s law:
- : surface normal
- : light direction
- : incident light intensity
- : albedo
Photometric Stereo
Suppose there are three light sources, , and we have the following measurements:
We can solve for by taking the dot product of and each light direction and then solving the system of equations.
Will not do this in the lecture.
Specular Reflection
- Mirror-like surface
- : view direction
- : reflection direction
- : angle between the incident light and the surface normal
Near-perfect mirror have a high light around .
common model:
- : specular reflection coefficient
- : shininess (imperfection of the surface)
- : incident light intensity
Phong illumination model
- Phong approximation of surface reflectance
- Assume reflectance is modeled by three compoents
- Diffuse reflection
- Specular reflection
- Ambient reflection
- Assume reflectance is modeled by three compoents
- : ambient reflection coefficient
- : ambient light intensity
- : diffuse reflection coefficient
- : specular reflection coefficient
- : shininess
- : incident light intensity
Many other models.
Measuring BRDF
Use Gonioreflectometer.
- Device for measuring the reflectance of a surface as a function of the incident and reflected angles.
- Can be used to measure the BRDF of a surface.
BRDF dataset:
- MERL dataset
- CURET dataset
Camera/Eye
DSLR Camera
- Pinhole camera model
- Lens
- Aperture (the pinhole)
- Sensor
- …
Digital Camera block diagram
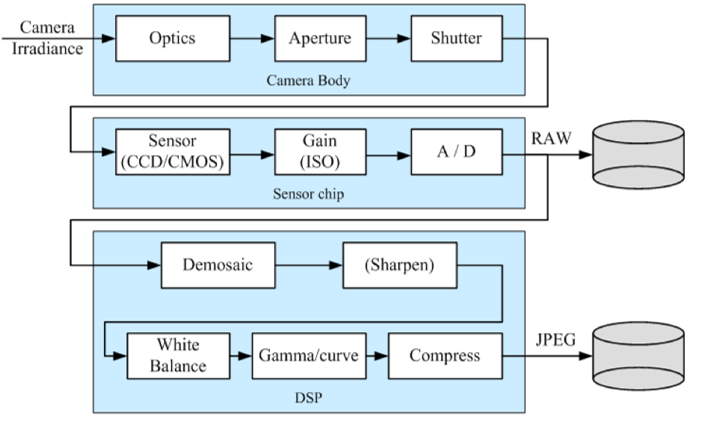
Scanning protocols:
- Global shutter: all pixels are exposed at the same time
- Interlaced: odd and even lines are exposed at different times
- Rolling shutter: each line is exposed as it is read out
Eye
- Pupil
- Iris
- Retina
- Rods and cones
- …
Eye Movements
- Saccade
- Can be consciously controlled. Related to perceptual attention.
- 200ms to initiation, 20 to 200ms to carry out. Large amplitude.
- Smooth pursuit
- Tracking an object
- Difficult w/o an object to track!
- Microsaccade and Ocular microtremor (OMT)
- Involuntary. Smaller amplitude. Especially evident during prolonged fixation.
Contrast Sensitivity
- Uniform contrast image content, with increasing frequency
- Why not uniform across the top?
- Low frequencies: harder to see because of slower intensity changes
- Higher frequencies: harder to see because of ability of our visual system to resolve fine features
Color Perception
Visible light spectrum: 380 to 780 nm
- 400 to 500 nm: blue
- 500 to 600 nm: green
- 600 to 700 nm: red
HSV model
We use Gaussian functions to model the sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths.
- Hue: color (the wavelength of the highest peak of the sensitivity curve)
- Saturation: color purity (the variance of the sensitivity curve)
- Value: color brightness (the highest peak of the sensitivity curve)
Color Sensing in Camera (RGB)
- 3-chip vs. 1-chip: quality vs. cost
Bayer filter:
- Why more green?
- Human eye is more sensitive to green light.
Color spaces
Images in python:
As matrix.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from skimage import io
def plot_rgb_3d(image_path):
image = io.imread(image_path)
r, g, b = image[:,:,0], image[:,:,1], image[:,:,2]
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(r.flatten(), g.flatten(), b.flatten(), c=image.reshape(-1, 3)/255.0, marker='.')
ax.set_xlabel('Red')
ax.set_ylabel('Green')
ax.set_zlabel('Blue')
plt.show()
plot_rgb_3d('image.jpg')Other color spaces:
- YCbCr (fast to compute, usually used in TV)
- HSV
- L*a*b* (CIELAB, perceptually uniform color space)
Most information is in the intensity channel.