CSE559A Lecture 26
Continue on Geometry and Multiple Views
The Essential and Fundamental Matrices
Math of the epipolar constraint: Calibrated case
Recall Epipolar Geometry
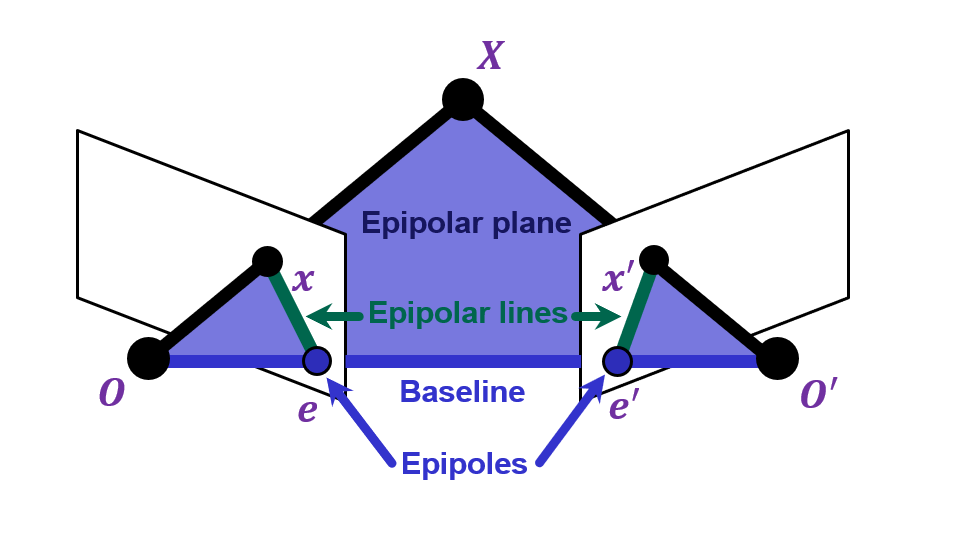
Epipolar constraint:
If we set the config for the first camera as the world origin and , and , then
Notice that
We denote the constraint defined by the Essential Matrix as .
is the epipolar line associated with ()
is the epipolar line associated with ()
and ( and don’t matter)
is singular (rank 2) and have five degrees of freedom.
Epipolar constraint: Uncalibrated case
If the calibration matrices and are unknown, we can write the epipolar constraint in terms of unknown normalized coordinates:
where ,
where is the Fundamental Matrix.
Properties of :
is the epipolar line associated with ()
is the epipolar line associated with ()
and
is singular (rank two) and has seven degrees of freedom
Estimating the fundamental matrix
Given: correspondences and
Constraint:
Each pair of correspondences gives one equation (one constraint)
At least 8 pairs of correspondences are needed to solve for the 9 elements of (The eight point algorithm)
We know needs to be singular/rank 2. How do we force it to be singular?
Solution: take SVD of the initial estimate and throw out the smallest singular value
Structure from Motion
Not always uniquely solvable.
If we scale the entire scene by some factor and, at the same time, scale the camera matrices by the factor of , the projections of the scene points remain exactly the same:
Without a reference measurement, it is impossible to recover the absolute scale of the scene!
In general, if we transform the scene using a transformation and apply the inverse transformation to the camera matrices, then the image observations do not change:
Types of Ambiguities
Affine projection : more general than orthographic
A general affine projection is a 3D-to-2D linear mapping plus translation:
In non-homogeneous coordinates:
Affine Structure from Motion
Given: 𝑚 images of 𝑛 fixed 3D points such that
Problem: use the 𝑚𝑛 correspondences to estimate 𝑚 projection matrices and translation vectors , and 𝑛 points
The reconstruction is defined up to an arbitrary affine transformation (12 degrees of freedom):
How many constraints and unknowns for images and points?
constraints and unknowns
To be able to solve this problem, we must have (affine ambiguity takes away 12 dof)
E.g., for two views, we need four point correspondences