CSE559A Lecture 19
Feature Detection
Behavior of corner features with respect to Image Transformations
To be useful for image matching, “the same” corner features need to show up despite geometric and photometric transformations
We need to analyze how the corner response function and the corner locations change in response to various transformations
Affine intensity change
Solution:
- Only derivative of intensity are used (invariant to intensity change)
- Intensity scaling
Image translation
Solution:
- Derivatives and window function are shift invariant
Image rotation
Second moment ellipse rotates but its shape (i.e. eigenvalues) remains the same
Scaling
Classify edges instead of corners
Automatic Scale selection for interest point detection
Scale space
We want to extract keypoints with characteristic scales that are equivariant (or covariant) with respect to scaling of the image
Approach: compute a scale-invariant response function over neighborhoods centered at each location and a range of scales , find scale-space locations where this function reaches a local maximum
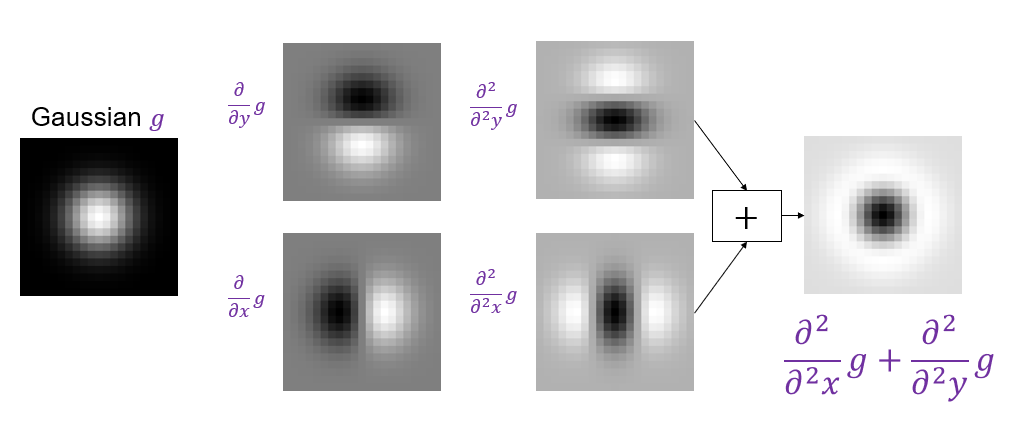
A particularly convenient response function is given by the scale-normalized Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter:
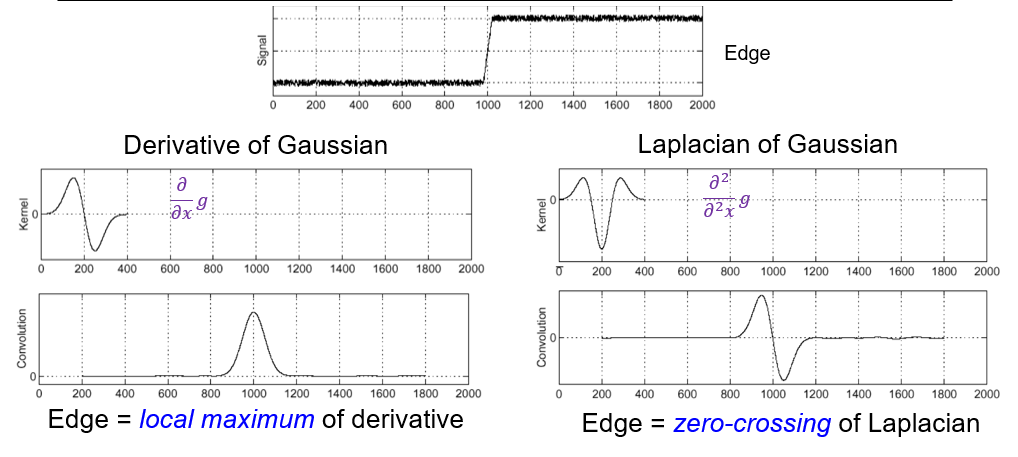
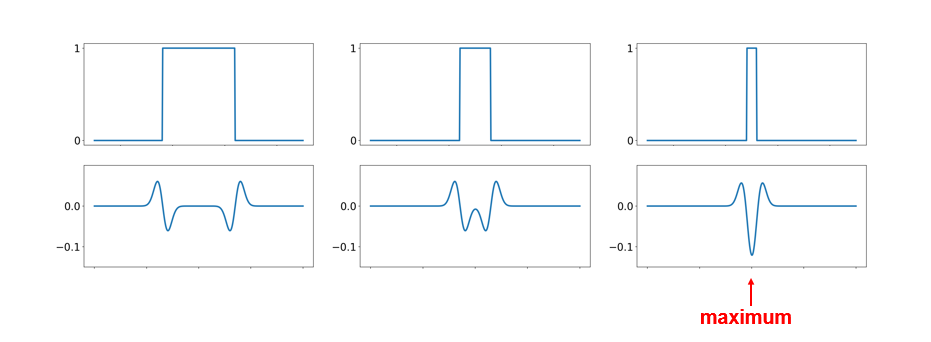
Edge detection with LoG
Blob detection with LoG
Difference of Gaussians (DoG)
DoG has a little more flexibility, since you can select the scales of the Gaussians.
Scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT)
The main goal of SIFT is to enable image matching in the presence of significant transformations
- To recognize the same keypoint in multiple images, we need to match appearance descriptors or “signatures” in their neighborhoods
- Descriptors that are locally invariant w.r.t. scale and rotation can handle a wide range of global transformations
Maximum stable extremal regions (MSER)
Based on Watershed segmentation algorithm
Select regions that are stable over a large parameter range