CSE559A Lecture 16
Dense image labelling
Semantic segmentation
Use one-hot encoding to represent the class of each pixel.
General Network design
Design a network with only convolutional layers, make predictions for all pixels at once.
Can the network operate at full image resolution?
Practical solution: first downsample, then upsample
Outline
- Upgrading a Classification Network to Segmentation
- Operations for dense prediction
- Transposed convolutions, unpooling
- Architectures for dense prediction
- DeconvNet, U-Net, “U-Net”
- Instance segmentation
- Mask R-CNN
- Other dense prediction problems
Fully Convolutional Networks
“upgrading” a classification network to a dense prediction network
- Covert “fully connected” layers to 1x1 convolutions
- Make the input image larger
- Upsample the output
Start with an existing classification CNN (“an encoder”)
Then use bilinear interpolation and transposed convolutions to make full resolution.
Operations for dense prediction
Transposed Convolutions
Use the filter to “paint” in the output: place copies of the filter on the output, multiply by corresponding value in the input, sum where copies of the filter overlap
We can increase the resolution of the output by using a larger stride in the convolution.
- For stride 2, dilate the input by inserting rows and columns of zeros between adjacent entries, convolve with flipped filter
- Sometimes called convolution with fractional input stride 1/2
Unpooling
Max unpooling:
- Copy the maximum value in the input region to all locations in the output
- Use the location of the maximum value to know where to put the value in the output
Nearest neighbor unpooling:
- Copy the maximum value in the input region to all locations in the output
- Use the location of the maximum value to know where to put the value in the output
Architectures for dense prediction
DeconvNet
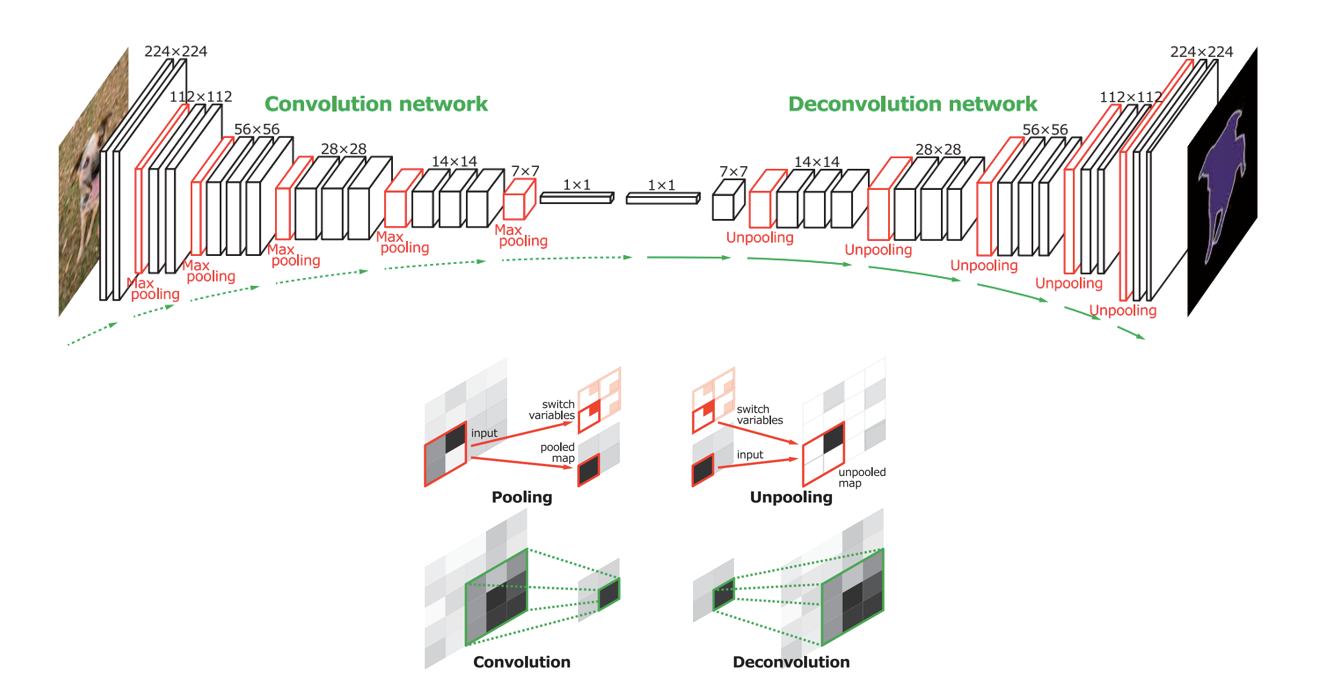
How the information about location is encoded in the network?
U-Net
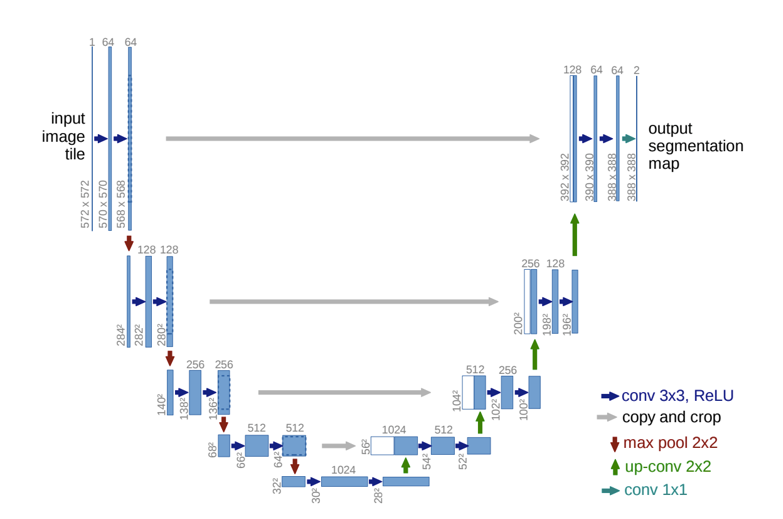
- Like FCN, fuse upsampled higher-level feature maps with higher-res, lower-level feature maps (like residual connections)
- Unlike FCN, fuse by concatenation, predict at the end
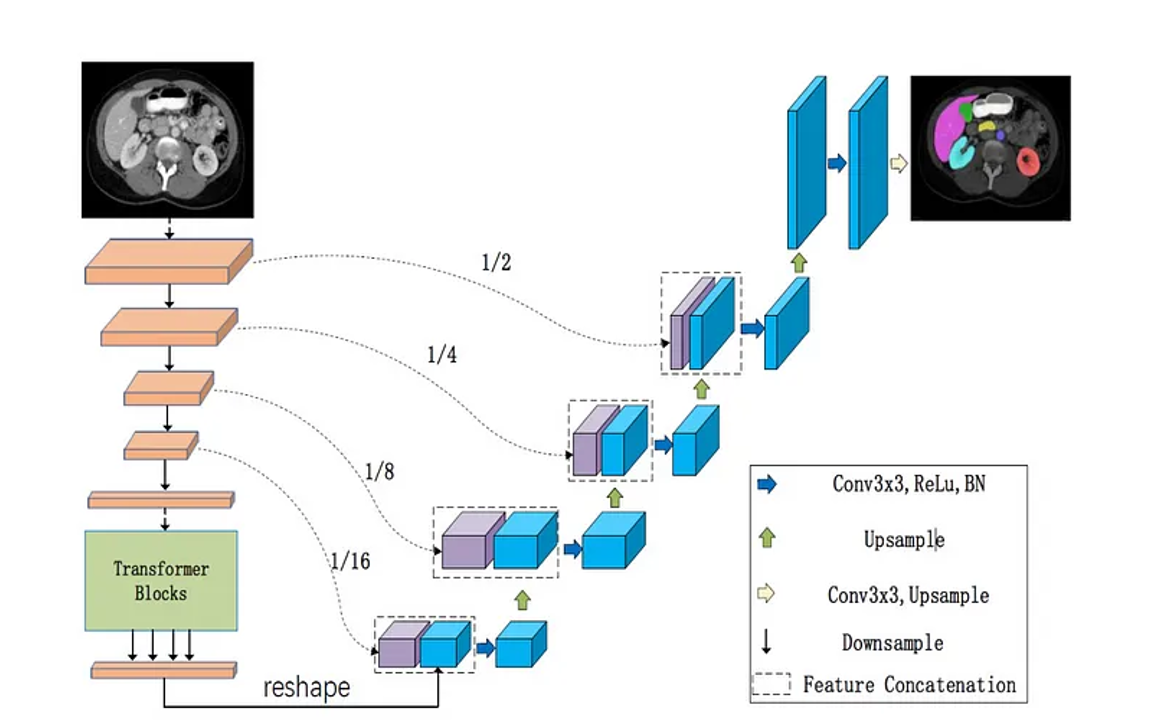
Extended U-Net Architecture
Many variants of U-Net would replace the “encoder” of the U-Net with other architectures.
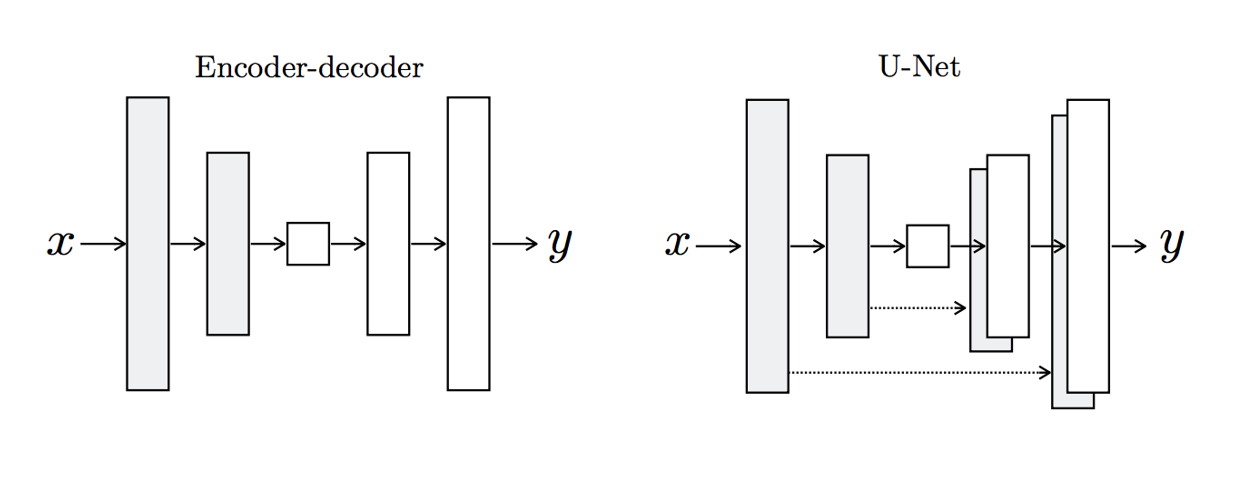
Encoder/Decoder v.s. U-Net
Instance Segmentation
Mask R-CNN
Mask R-CNN = Faster R-CNN + FCN on Region of Interest
Extend to keypoint prediction?
- Use a similar architecture to Mask R-CNN
Continue on Tuesday
Other tasks
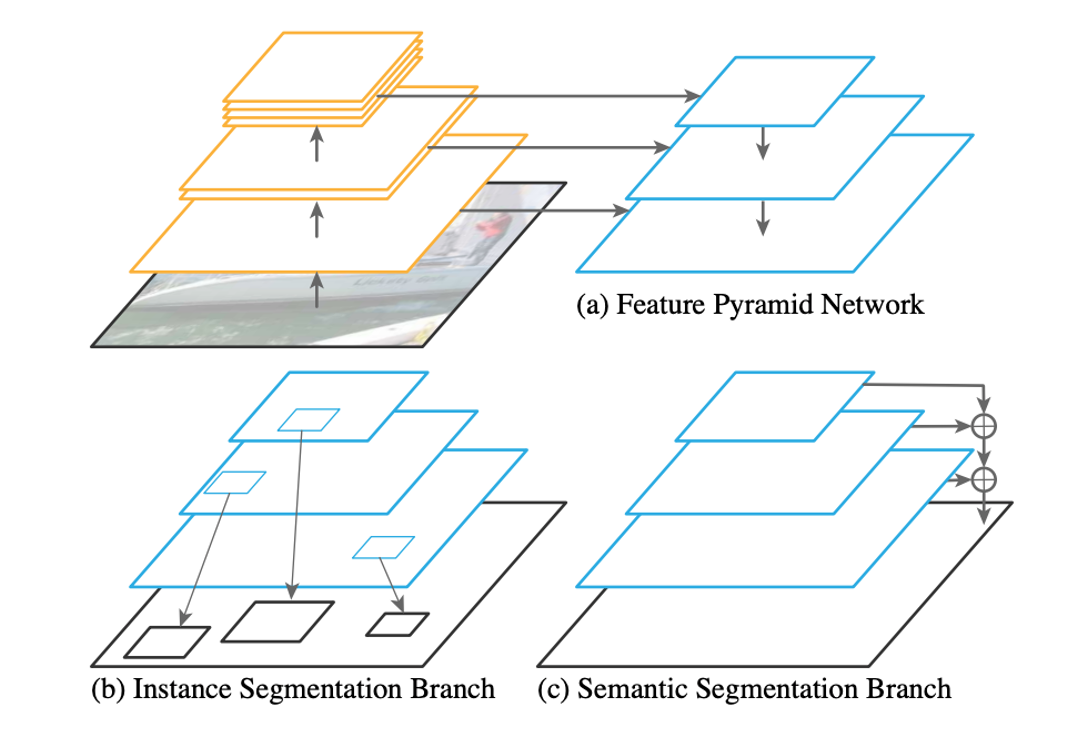
Panoptic feature pyramid network
Depth and normal estimation
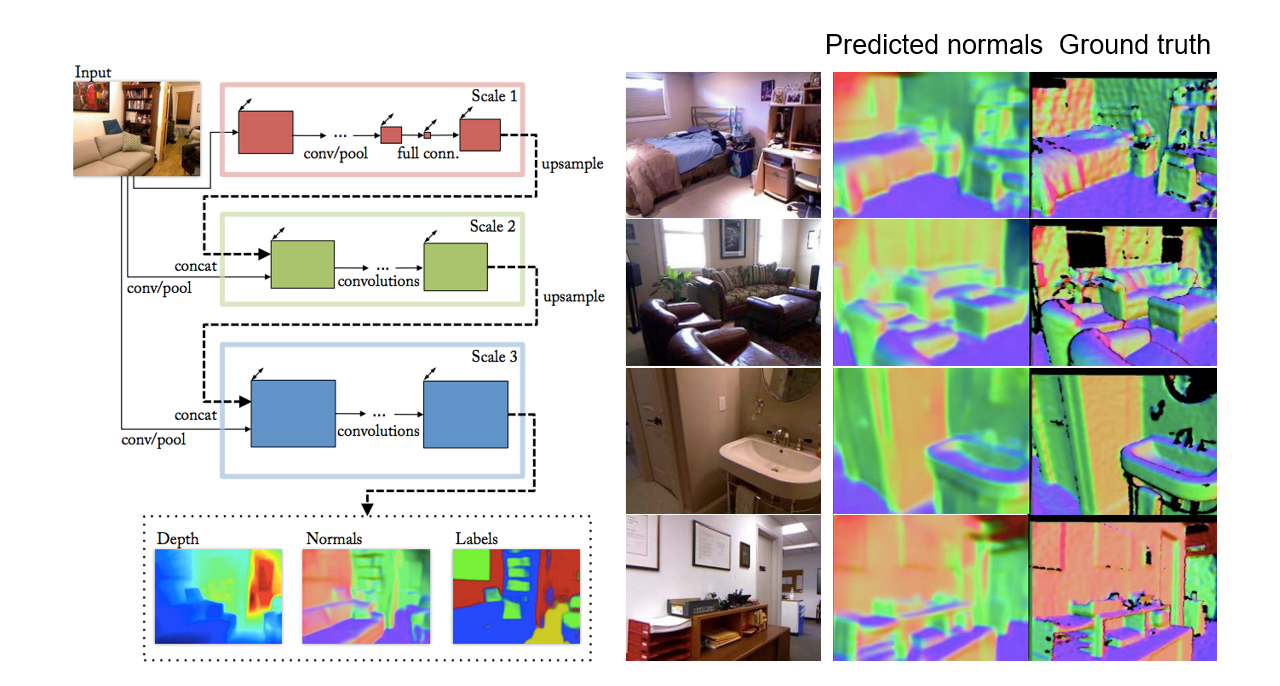
D. Eigen and R. Fergus, Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-Scale Convolutional Architecture, ICCV 2015
Colorization
R. Zhang, P. Isola, and A. Efros, Colorful Image Colorization, ECCV 2016