CSE559A Lecture 12
Transformer Architecture
Outline
Self-Attention Layers: An important network module, which often has a global receptive field
Sequential Input Tokens: Breaking the restriction to 2d input arrays
Positional Encodings: Representing the metadata of each input token
Exemplar Architecture: The Vision Transformer (ViT)
Moving Forward: What does this new module enable? Who wins in the battle between transformers and CNNs?
The big picture
CNNs
- Local receptive fields
- Struggles with global content
- Shape of intermediate layers is sometimes a pain
Things we might want:
- Use information from across the image
- More flexible shape handling
- Multiple modalities
Our Hero: MultiheadAttention
Use positional encodings to represent the metadata of each input token
Self-Attention layers
Comparing with ways to handling sequential data
RNN
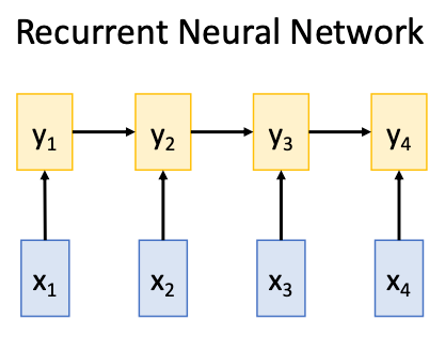
Works on Ordered Sequences
- Good at long sequences: After one RNN layer sees the whole sequence
- Bad at parallelization: need to compute hidden states sequentially
1D conv
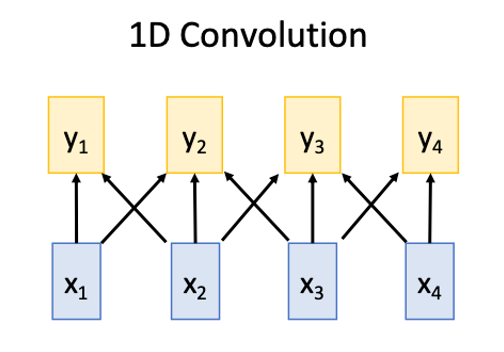
Works on Multidimensional Grids
- Bad at long sequences: Need to stack may conv layers or outputs to see the whole sequence
- Good at parallelization: Each output can be computed in parallel
Self-Attention
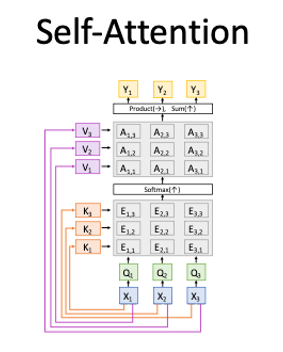
Works on Set of Vectors
- Good at Long sequences: Each output can attend to all inputs
- Good at parallelization: Each output can be computed in parallel
- Bad at saving memory: Need to store all inputs in memory
Encoder-Decoder Architecture
The encoder is constructed by stacking multiple self-attention layers and feed-forward networks.
Word Embeddings
Translate tokens to vector space
class Embedder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, d_model):
super().__init__()
self.embed=nn.Embedding(vocab_size, d_model)
def forward(self, x):
return self.embed(x)Positional Embeddings
The positional encodings are a way to represent the position of each token in the sequence.
Combined with the word embeddings, we get the input to the self-attention layer with information about the position of each token in the sequence.
The reason why we just add the positional encodings to the word embeddings is perhaps that we want the model to self-assign weights to the word-token and positional-token.
Query, Key, Value
The query, key, and value are the three components of the self-attention layer.
They are used to compute the attention weights.
class SelfAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.d_k = d_k
self.q_linear = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k)
self.k_linear = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k)
self.v_linear = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.out = nn.Linear(d_k, d_k)
def forward(self, q, k, v, mask=None):
bs = q.size(0)
k = self.k_linear(k)
q = self.q_linear(q)
v = self.v_linear(v)
# calculate attention weights
outputs = attention(q, k, v, self.d_k, mask, self.dropout)
# apply output linear transformation
outputs = self.out(outputs)
return outputsAttention
def attention(q, k, v, d_k, mask=None, dropout=None):
scores = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(d_k)
if mask is not None:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1)
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
scores = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
if dropout is not None:
scores = dropout(scores)
outputs = torch.matmul(scores, v)
return outputsThe query, key are used to compute the attention map, and the value is used to compute the attention output.
Multi-Head self-attention
The multi-head self-attention is a self-attention layer that has multiple heads.
Each head has its own query, key, and value.
Computing Attention Efficiency
- the standard attention has a complexity of
- We can use sparse attention to reduce the complexity to