CSE4303 Introduction to Computer Security (Lecture 3)
Network attacks
Internet Infrastructures
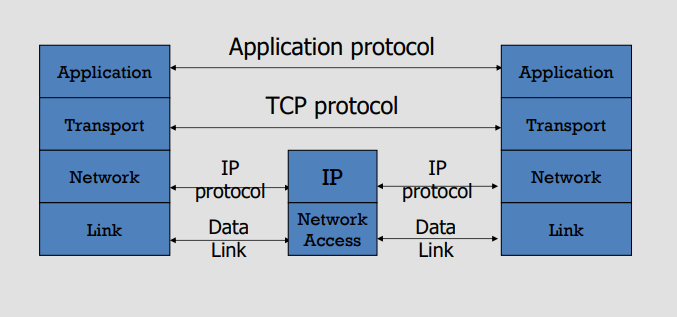
Local and interdomain routing
- TCP/IP for routing and messaging
- BGP for routing announcements
Domain Name System
- Find IP address from symbolic name (cse.wustl.edu)
Media Access Control (MAC) addresses in the network access layer
- Associated w/ network interface card (NIC)
- 00-50-56-C0-00-01
IP addresses for the network layer
- IPv4(32 bit) vs IPv6(128 bit)
- 128.1.1.3 vs fe80::fc38:6673:f04d:b37b%4
IP addresses + ports for the transport layer
- E.g., 10.0.0.2:8080
Domain names for the application/human layer
- E.g., www.wustl.edu
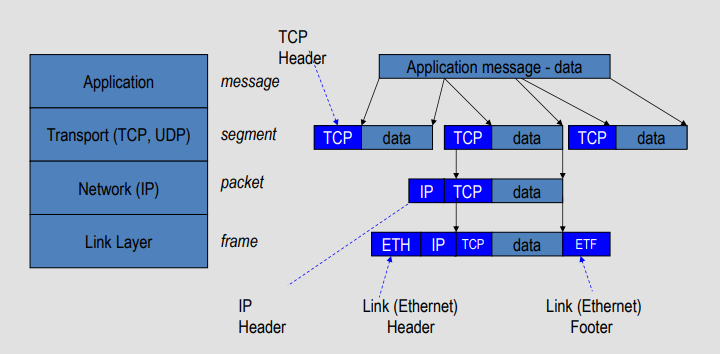
Wireshark
Wireshark is a packet sniffer and protocol analyzer
- Captures and analyzes frames
- Supports plugins
Usually required to run with administrator privileges
Setting the network interface in promiscuous mode captures traffic across the entire LAN segment and not just frames addressed to the machine
Examining the link layer
When a packet arrives at the destination subnet, MAC address is used to deliver the packet
ARP: Address Resolution Protocol
- Each IP node (Host, Router) on LAN has ARP table
- ARP Table: IP/MAC address mappings for some LAN nodes
< IP address; MAC address; TTL>- TTL (Time To Live): time after which address mapping will be forgotten (typically 20 min)
Lack of Source Authentication - ARP Spoofing (ARP Poisoning)
Send fake or ‘spoofed’, ARP messages to an Ethernet LAN.
- To have other machines associate IP addresses with the attacker’s MAC
Legitimate use
- Implementing redundancy and fault tolerance
ARP Poisoning (Spoofing) Defense
Prevention
- Static ARP table
- DHCP Certification (use access control to ensure that hosts only use the IP addresses assigned to them, and that only authorized DHCP servers are accessible).
Detection
- Arpwatch (sending email when updates occur)
Examining the network layer
Internet Protocol (IP)
Connectionless
- Unreliable
- Best effort
Notes:
- src and dest ports not parts of IP hdr
IP Protocol Functions (Summary)
Routing
- IP host knows location of router (gateway)
- IP gateway must know route to other networks
Fragmentation and reassembly
- If max-packet-size less than the user-data-size
Error reporting
- ICMP packet to source if packet is dropped
TTL field: decremented after every hop
- Packet dropped if TTL=0. Prevents infinite loops
Problem: no src IP authentication
Client is trusted to embed correct source IP
-
Easy to override using raw sockets
-
Libnet: a library for formatting raw packets with arbitrary IP headers
-
Scapy: a python library for packet crafting
Anyone who owns their machine can send packets with arbitrary source IP
- … response will be sent back to forged source IP
Implications:
- Anonymous DoS attacks;
- Anonymous infection attacks (e.g. slammer worm)